7 of the world's best free patent databases
The choice of patent database depends largely on the purpose of the search, as well as the type of patent search. For example, for a prior art search for current litigation, you may want to choose a patent database that covers patent documents from most patent offices. Here, doing your best will be key.
For example, for FTO searches, this depends on the specific geographical location - you may want to use a patent database that provides patents from that specific country in the best searchable way, but of all the patent databases in the world, few have indexed German patents well, and few have indexed Chinese patents.
If you just want to use a basic database and your goal is just to quickly get some clues, then Google Patents will be your first choice. Otherwise, if you want to search for a specific industry, then you may need a more specialized patent database.
1. Free Patent Database
Free patent search websites are ideal for getting quick leads. There is no point in paying for a huge database just to search one or two patents. Listed below are some free patent databases that can help you with patent data search and analysis.
- Google Patents
- Espacenet
- USPTO Web Patent Database
- PQAI
- Patentscope by WIPO
- WIPO's INSPIRE
- Lens.org
1. Google Patents
Google Patents was established on December 14, 2006. Due to its fast patent search speed, it quickly became the first choice for most industry insiders. Users only need to enter the patent number to be searched in the address bar of the browser and press the Enter key. The first search result that appears in Google Patents is always directly related to the patent. It is very simple and convenient.
Google Patents is committed to expanding the coverage of its patent database, which now includes the full text of over 87 million patents from patent offices in 17 different countries, including:
- United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO)
- European Patent Office (EPO)
- China National Intellectual Property Administration (CNIPA)
- Japan Patent Office (JPO)
- Korean Intellectual Property Office (KIPO)
- World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO)
- German Patent and Marketing Fund (DPMA)
- Canadian Intellectual Property Office (CIPO)
- and patent data from other national patent offices including Russia, the United Kingdom, France, Spain, Belgium, Denmark, Finland, Luxembourg and the Netherlands.
Google Patents allows users to search for patents based on the following variables:
- date
- Assignee
- Inventor
Users can further sort using filters:
- Patent Office
- Status (granted/applied)
- Type (patent/design)
- When viewing a specific keyword, patents can be opened in the sidebar while keeping the patent list intact.
Google also provides non-patent data, such as data from Google Scholar, where users can search for research papers containing keywords and save them in PDF format. Google Patents can also translate patent language into any language of the user's choice, including Chinese.
Google also provides users with an illustrative chart with keywords that you can view by assignee, inventor, and CPC classification.
2. Espacenet
Espacenet was born out of a collaboration between the European Patent Office (EPO) and the European Patent Organization. Espacenet was officially opened to the public in 1998 with the aim of "revolutionizing the way the public accesses international patent information".
Espacenet recently upgraded its system and currently provides a database of more than 110 million patents from 97 countries. At the same time, Espacenet uses an excellent machine translation system and has become the most effective patent translation in the global patent database. Users can even use language combinations for patent searches, such as EnglishàArabic or ChineseàEnglish. Espacenet covers translations between English and 31 other languages. The translation engine is "specifically built to handle complex technical patent vocabulary" and uses "millions of official, manually translated patent documents" to train the translation engine.
To search for patents on Espacenet:
- A. Smart search: In smart search, you can enter up to 20 search terms. Each searchable condition can contain up to 10 terms, with or without field identifiers.
- B. Advanced search: In advanced search, you can use the following variables/categories to perform a deeper search:
- title
- summary
- Public Number
- Application Number
- Priority number
- Publication Date
- applicant
- Inventor
- CPC Classification Number
- IPC Classification Number
- C. Classification search: Search patents based on CPC classification numbers.
For those who have never conducted a patent search, or do not know how to do one, Espacenet has a video tutorial on almost every page. Espacenet also provides the option to download the original patent in PDF format. In addition, it is possible to view the patent family of a specific patent.
Another interesting and useful feature of Espacenet is its “Citation View”, which facilitates prior art searches. It provides all cited patent families on one interface and separates citations into inventor citations and examiner citations, which is rarely seen in other databases. Espacenet also provides users with a “My Patent List” to view all searched patents. The homepage also features information on maintenance fees, etc. Users can also view all searched patents in the “History Search” tab.
3. USPTO
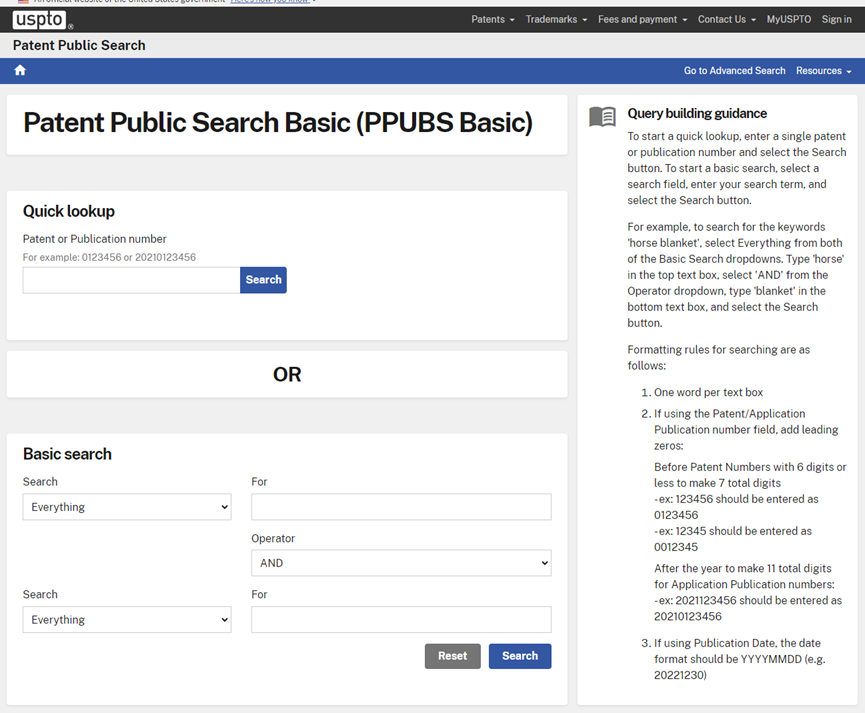
The United States Patent and Trademark Office is a federal agency of the United States government responsible for granting U.S. patents and registering trademarks.
The website not only displays published and applied patents, but also provides information on what a patent is, whether your idea can be patented, the patent application process, patent maintenance fees, etc., basically covering a complete patent application process and FAQs. At the same time, users can also find information about trademarks and other intellectual property rights, such as intellectual property policies, international affairs, intellectual property research and training, trademark application procedures, trademark maintenance and trademark basics.
Enter a keyword in the search bar on the homepage to find related patents.
The search bar at the top of the page allows you to search with CPC as a keyword, and you can also find information about patents and trademarks in the "Quick Find" column, which is the main advantage of the USPTO. As a government website, all patents have accurate and up-to-date status. Although the interface is very simple and the website is not suitable for patent analysis, the exact legal status of each patent and a detailed description can be obtained.
4. PQAI
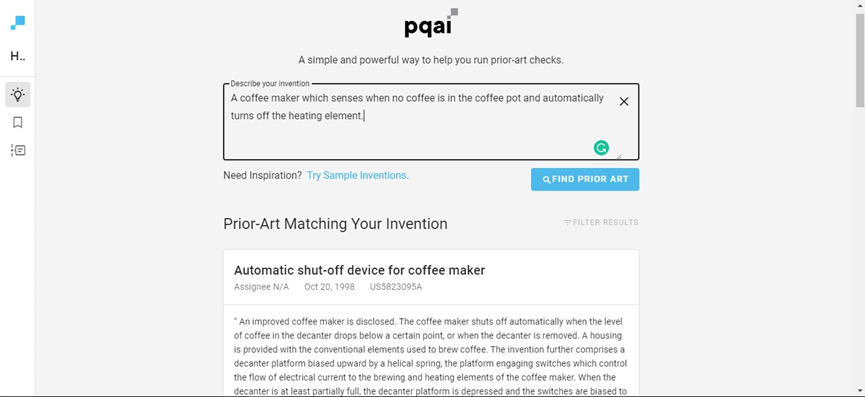
PQAI is an open source platform developed by AT&T in the United States to improve the patent process through better prior art search and analysis.
Patent language and complex database operations discourage many users. However, PQAI uses artificial intelligence and natural language processing technology to make searching simple and easy for inventors. Anyone who can use layman's language to describe their invention and search, PQAI can provide 10 or more of the most relevant patent search results.
The biggest problem that inventors face before filing a patent application is how to keep their innovative ideas confidential. In view of this, the security features of the search tool are crucial, which is why PQAI is an ideal choice for inventors and prior art search. PQAI never records any user's search queries or results unless the user explicitly requests to save the search history.
PQAI also provides "invention samples" in the search column for users to try, so that users can better understand how PQAI works.
5. Patentscope by WIPO
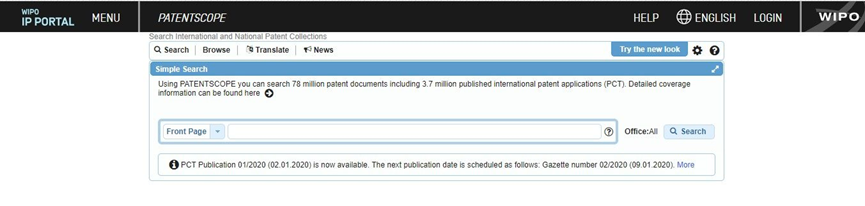
The World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) is one of the 15 agencies of the United Nations. It is headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland and currently has 192 member states. It was established on July 14, 1967. WIPO has a huge database that can search not only patents, but also trademarks and industrial designs.
WIPO's Patentscope is very powerful, providing more than 83 million patent documents from multiple participating patent offices, which can be searched in 9 different languages. The above interface shows the default simple search, which is one of the four search methods of Patentscope. You can also choose to perform a quick search or an advanced search.
Patentscope's quick search option is very easy to use. You can use the name field to search for inventors, assignees, applicants, etc. If you select FrontPage in the drop-down menu, you can search patent abstracts using only keywords. In advanced patent search, you can also use operators and stemming functions. When searching with stems, Patentscope will use the keyword as the root and search for other terms derived from it. For example, if you enter the word "cell phone", Patentscope will automatically search for "mobile phone" and so on.
6. WIPO INSPIRE
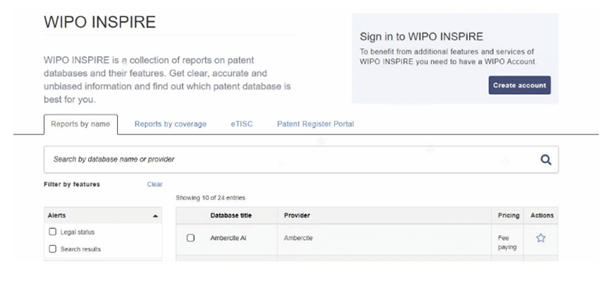
WIPO launched the INSPIRE (Patent Information Report Search) tool in November 2020. After using this tool, many people said that it is the ultimate database tool and a search master in the patent database!
WIPO's goal has always been to accelerate the innovation process, and this effort is also reflected in creating more suitable search tools for users according to their needs. Whether you are a novice or an expert in patent search, INSPIRE can help you find the exact method that suits your current needs. By setting filters, INSPIRE can also provide you with a list of the most suitable search systems.
Filters include those that offer machine translation, cross-language semantic search or search in non-Latin characters, and there are many other filters to choose from.
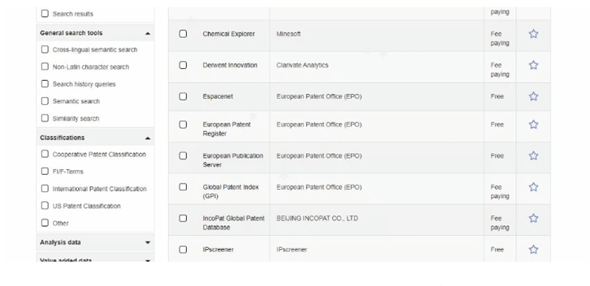
Not only that, but the tabular reports that are subsequently generated allow for an at-a-glance comparison of selected resources and their prices. Opening the individual database reports also provides more detailed information from the suppliers. So far, INSPIRE has proven to be extremely useful and much needed by IP personnel.
7. Lens.org
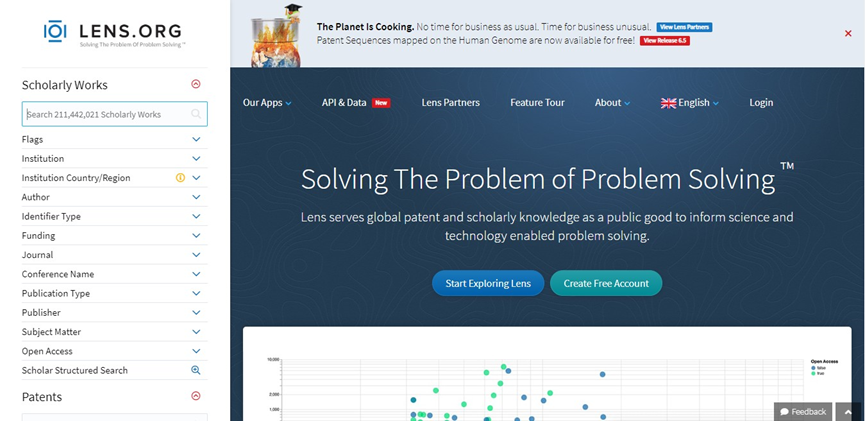
Lens.org is an open source database project developed by Cambia and Queensland University of Technology. It started in 2000 and currently stores more than 119 million documents from 105 jurisdictions. One of the main features that distinguishes Lens.org from other websites is that it provides users with citation data and non-patent literature. Lens.org has a clean and friendly user interface. Although its functions are complex, the webpage is not cluttered at all.
Lens.org is the best choice for drug patent search and is one of the few databases in the world that can be searched by gene sequence. Users can search according to the following parameters:
- full text
- title
- summary
- Inventor
- Applicant/Assignee
- Public Number
- Application Number
The following filters can be applied in patent searches:
- Label
- mechanism
- Country/Region of Institution
- author
- Identifier Type
- funds
- publication
- Meeting Name
- Public Type
- Publisher
- theme
- Open Access
- Query Tool
- New Structure
- Year of publication
Users can also search for lapsed, abandoned or expired US patents by using INPADOC’s patent status and patent family information services. Patent families can be visualized using a graphical tree in pdf format. In addition, dynamic charts are another feature of lens.org that is useful when analyzing patent information.
One of the highlights of Lens.org is that users can create a list of patents and analyze them individually.
联系咨询
 | Get exact prices For the country / regionE-mail: mail@yezhimaip.com |
